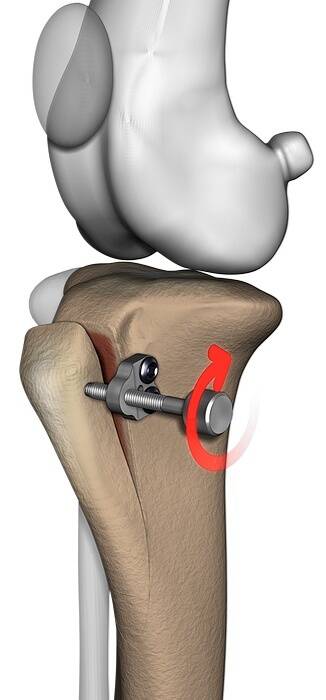
Shifting the tibial tuberosity using the Trans TOOL.
{ Article for the journal Modern Veterinary Clinic 2023 }
Patellar luxation is a condition in which the patella, instead of moving anatomically in the intercondylar groove, falls out of it and dislocation occurs.
Medial dislocation is most common, although lateral luxation is also seen. It occurs in all dog breeds, but it is much more common in small and miniature breeds.
One of the most popular treatments for a patellar luxation is to shift the tibial tuberosity. It consists in incomplete, vertical cutting of the tibia, similarly to the TTA procedure (Tibial Tuberosity Advancement) and its displacement in the frontal plane.
The cut is made in 30 percent of the total width of the tibia in the lateral view.
During preoperative planning, the surgeon predetermines the required offset distance, but this requires intraoperative verification. Maintaining the required shift during the test using the hand is difficult and imprecise, while stabilizing the tuberosity after transposition with the implant makes it difficult to correct it in the event of further abnormal movement of the patella in the patellofemoral groove.
In this case, we need to remove the implant, increase the offset distance, and reinsert the implant in a different location. This leaves unnecessary bone loss and limits the number of attempts we can make.
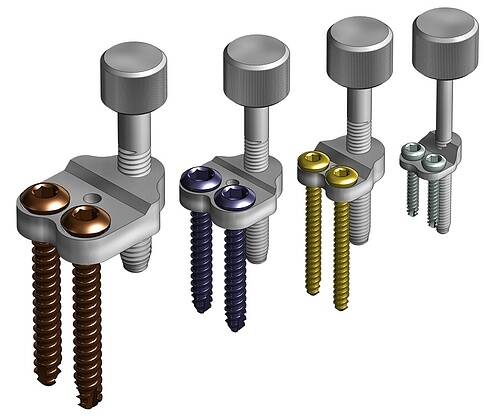
The solution to this problem is the use of the Trans TOOL - a special device for the transposition of the tibial tuberosity, which enables precise performance of the procedure and checking its effect during the operation. This instrument is available in four different sizes.
Depending on the size of the patient, we can choose one of four systems:
1.5 / 2.0 (miniature and small breeds), 2.4 / 2.7 (medium breeds) and 3,5 (large breeds).